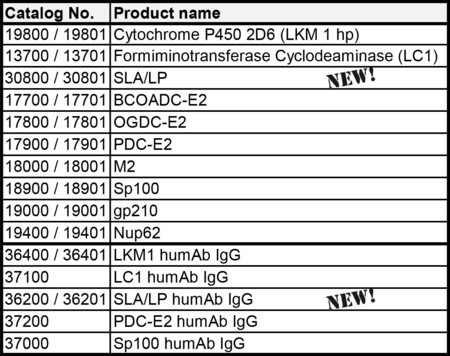
抗可溶性肝抗原/肝胰抗原(SLA/LP)抗原和人源嵌合抗体
Diarect公司隆重推出抗可溶性肝抗原/肝胰抗原(SLA/LP)抗原和人源嵌合抗体
抗SLA/LP抗体的靶抗原参与selenprotein(一种UGA抑制物,tRNA相关蛋白)生物合成的调节,早期的研究也表明抗 SLA抗体有可能参与了对肝细胞的破坏,因此推测抗SLA/LP抗体与自身免疫性肝炎(AIH)的发病机制有关。虽然AIH存在种类较多的自身抗体,但多数自身抗体并非AIH特异性抗体。抗SLA/LP抗体为AIH高度特异性自身抗体,在AIH相关自身抗体中具有诊断价值。抗 SLA/LP抗体在 AIH中的阳性率为10%~30%,该抗体多出现在ANA, SMA和抗LKM-1抗体阴性的AIH患者血清中。抗SLA/LP抗体为AIH-Ⅲ型的血清学标志,临床上常用于AIH的诊断和鉴别诊断。阳性患者多为年轻女性,多伴有高免疫球蛋白血症。约30%的AIH-Ⅲ型仅该抗体阳性,而缺乏所有其他自身抗体标志,但对免疫抑制治疗有效,抗SLA抗体测定对发现这一部分AIH患者有重要意义。
New additions to DIARECT’s liver panel: SLA/LP antigen and human chimeric SLA/LP antibody
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic, progressive inflammation of the liver and was first described in 1965 by Mackay et al. It was hypothesized that pathogenesis comprises environmental triggers, failure of immune tolerance mechanism and genetic predisposition (Vergani et al. 2002).
The disease does not exhibit pathognomonic symptoms; therefore diagnosis should combine clinical, serological, histological and genetic parameters. When diagnosed correctly, AIH is usually responsive to immuno-suppressive therapy. In the end stage the only therapeutic approach remaining is a liver transplantation (Costa et al. 2000).
Two types of AIH have been classified: AIH-2 and AIH-1. AIH-1 is most common and characterized by antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and smooth muscle antibodies (SMA). Detection of SLA/LP autoantibodies indicate a more severe progression of both types of the disease. AIH-2 is typified by seropositivity of patients with LKM1 and LC1 autoantibodies (Costa et al. 2000; Gelpi et al. 1992).
SLA/LP was first reported in supernatant of liver and kidney homogenates by Manns et al. 1987. It is a cytosolic soluble liver antigen / liver pancreas antigen specifically detected in about 20% of the patients with AIH. The target of anti-SLA/LP is a approx. 50-kDa UGA serine tRNA-associated protein complex (tRNP(Ser) Sec) (Wies et al. 2000). Costa et al. 2000 showed a high specificity and frequency (47, 5 %) of anti-tRNP (Ser) Sec autoantibodies for severe forms of type-1 AIH.
The RNA is a UGA suppressor serine tRNA (tRNA (Ser) Sec) and it functions in the pathway of selenoprotein synthesis in human cells. The tRNA is a requisite for co-translational incorporation of selenocystein into growing polypeptide chains. Therefore the RNA is shared with serine to seryl-tRNA and then converted to selenocysteyl-tRNA sec by the action of a selenocysteine synthase (Bock et al. 1991).
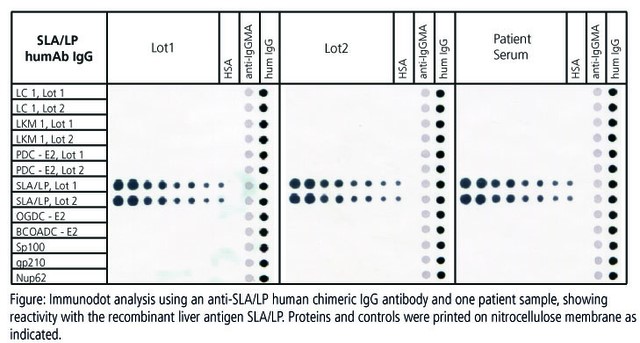
Diagnostic assays for autoantibody detection requires reference material to determine cut-off values and assay integrity. Mostly, pools of disease state serum or plasma are used. Main drawbacks of these standards are limited availability and variability. More consistent is the advanced use of chimeric monoclonal antibodies as positive controls in IVD kit development. This approach ensures consistent concentration, specificity and avidity, and furthermore eliminates safety and ethical concerns.